Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshioka, Kenichi*; Kikuchi, Tsukasa*; Gunji, Satoshi*; Kumanomido, Hironori*; Mitsuhashi, Ishi*; Umano, Takuya*; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Okajima, Shigeaki; Fukushima, Masahiro; Nagaya, Yasunobu; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(2), p.282 - 293, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have developed a void reactivity evaluation method by using modified conversion ratio measurements in a light water reactor (LWR) critical lattice. Assembly-wise void reactivity is evaluated from the "finite neutron multiplication factor", 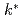 , deduced from the modified conversion ratio of each fuel rod. The distributions of modified conversion ratio and
, deduced from the modified conversion ratio of each fuel rod. The distributions of modified conversion ratio and 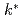 on a reduced-moderation LWR lattice, for which the improvement of negative void reactivity is a serious issue, were measured. Measured values were analyzed with a continuous-energy Monte Carlo method. The measurements and analyses agreed within the measurement uncertainty. The developed method is useful for validating the nuclear design methodology concerning void reactivity.
on a reduced-moderation LWR lattice, for which the improvement of negative void reactivity is a serious issue, were measured. Measured values were analyzed with a continuous-energy Monte Carlo method. The measurements and analyses agreed within the measurement uncertainty. The developed method is useful for validating the nuclear design methodology concerning void reactivity.
Nakatsuka, Toru; Tamai, Hidesada; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
The subchannel analysis code NASCA was applied to critical power prediction of 37-rod tight-lattice bundle experiments which JAERI has been carrying out to confirm the thermal-hydraulic feasibility of the RMWR. The NASCA can yield good predictions of critical power for the gap width of 1.3 mm while the prediction accuracy of critical power deteriorated in case of the gap width of 1.0 mm. Predicted BT positions agree with the experimental results. Models in the code will be improved to consider the effect of the gap width based on further studies in the future.
Liu, W.; Onuki, Akira; Tamai, Hidesada; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2005/10
In this research, the newest version of critical power correlation for tight-lattice rod bundles is proposed by using 7-rod and 37-rod bundle data derived in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). For comparatively high mass velocity region, the correlation is written in local critical heat flux - critical quality type. For low mass velocity region, it is written in critical quality - annular flow length type. The correlation is verified by JAERI data and Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory data. It is confirmed the correlation is able to give good prediction for the effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure and heated equivalent diameter on critical power. The correlation is further implemented into TRAC code to analyze flow decrease and power increase transients. It is confirmed transient BT can be predicted within the accuracy of the implemented critical power correlation.
Kaneko, Tetsuji; Tsukatani, Ichiro; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
JAERI-Research 2005-005, 23 Pages, 2005/03
Fuel elements used in The Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) have the lamellar structure consisting of MOX pellets and UO blankets in order to attain the high breeding ratio and high burn-up simultaneously. It is a characteristic of the fuel elements that there is high thermal stress caused by inhomogeneous linear power density along the longitudinal direction of the fuel rod. Therefore, it is important to evaluate the local deformation behavior due to the transient temperature distribution. To estimate the thermal deformation behavior, the temperature and stress distribution of the fuel cladding tube assumed in the designed reactor were analyzed. Moreover, basic physical properties and mechanical properties for analyzing the deformation behavior were obtained by experiment using fuel cladding tubes made of candidate alloys. In addition, the appropriate experimental conditions for realizing the practical thermal deformation behavior of the fuel cladding tube was selected by adjusting the testing temperature distribution based on data obtained with thermal analysis.
blankets in order to attain the high breeding ratio and high burn-up simultaneously. It is a characteristic of the fuel elements that there is high thermal stress caused by inhomogeneous linear power density along the longitudinal direction of the fuel rod. Therefore, it is important to evaluate the local deformation behavior due to the transient temperature distribution. To estimate the thermal deformation behavior, the temperature and stress distribution of the fuel cladding tube assumed in the designed reactor were analyzed. Moreover, basic physical properties and mechanical properties for analyzing the deformation behavior were obtained by experiment using fuel cladding tubes made of candidate alloys. In addition, the appropriate experimental conditions for realizing the practical thermal deformation behavior of the fuel cladding tube was selected by adjusting the testing temperature distribution based on data obtained with thermal analysis.
Liu, W.; Kureta, Masatoshi; Onuki, Akira; Akimoto, Hajime
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(1), p.40 - 49, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this research, critical power correlation for tight-lattice rod bundles is newly proposed using 7-rod axially uniform-heated data, 7-rod and 37-rod axially double-humped-heated data at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). For low mass velocity region ( 300 kg/m
300 kg/m s), the correlation is written in critical quality - annular flow length type. For high mass velocity region (
s), the correlation is written in critical quality - annular flow length type. For high mass velocity region ( 300 kg/m
300 kg/m s), it is written in local critical heat flux - critical quality type. The standard deviation of ECPR (Experimental Critical Power Ratio) to the whole JAERI data (694 data points) is 6%. The correlation is verified by Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory data (177 points, standard deviation: 7.7%). The correlation is confirmed being able to give good prediction for the effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure and heated equivalent diameter on critical power. The applicable range of the correlation is: gap between rods from 1.0 to 2.29 mm, heated length from 1.26 to 1.8 m, mass velocity from 150 to 2000 kg/m
s), it is written in local critical heat flux - critical quality type. The standard deviation of ECPR (Experimental Critical Power Ratio) to the whole JAERI data (694 data points) is 6%. The correlation is verified by Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory data (177 points, standard deviation: 7.7%). The correlation is confirmed being able to give good prediction for the effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure and heated equivalent diameter on critical power. The applicable range of the correlation is: gap between rods from 1.0 to 2.29 mm, heated length from 1.26 to 1.8 m, mass velocity from 150 to 2000 kg/m s and pressure from 2 to 11 MPa.
s and pressure from 2 to 11 MPa.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Akie, Hiroshi; Kugo, Teruhiko; Yonomoto, Taisuke; Kureta, Masatoshi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Araya, Fumimasa; Okajima, Shigeaki; et al.
JAERI-Research 2004-008, 383 Pages, 2004/06
The present report contains the achievement of "Research and Development on Reduced-Moderation Light Water Reactor with Passive Safety Features", which was performed by Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), Hitachi Ltd., Japan Atomic Power Company and Tokyo Institute of Technology in FY2000-2002 as the innovative and viable nuclear energy technology (IVNET) development project operated by the Institute of Applied Energy (IAE). In the present project, the reduced-moderation water reactor (RMWR) has been developed to ensure sustainable energy supply and to solve the recent problems of nuclear power and nuclear fuel cycle, such as economical competitiveness, effective use of plutonium and reduction of spent fuel storage. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as high burnup, long operation cycle, multiple recycling of plutonium (Pu) and effective utilization of uranium resources based on accumulated LWR technologies.
Kaneko, Tetsuji; Tsukatani, Ichiro; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
JAERI-Tech 2004-035, 18 Pages, 2004/03
Fuel elements used in the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) have the stacking structure consisting of MOX pellets and UO blankets in a fuel rod in order to attain the high breeding ratio and high burn-up simultaneously. It is a characteristic of the fuel elements that there is high thermal stress caused by inhomogeneous linear power density along the longitudinal direction of the fuel rod in comparison with the present LWR fuels. For this reason, it is important to estimate local deformation behavior of the fuel cladding tube with temperature difference caused by MOX pellet and UO
blankets in a fuel rod in order to attain the high breeding ratio and high burn-up simultaneously. It is a characteristic of the fuel elements that there is high thermal stress caused by inhomogeneous linear power density along the longitudinal direction of the fuel rod in comparison with the present LWR fuels. For this reason, it is important to estimate local deformation behavior of the fuel cladding tube with temperature difference caused by MOX pellet and UO blanket. The testing machine was designed to investigate thermal-fatigue behavior under biaxial stress condition. The testing machine consists of the temperature distribution control unit, low cycle fatigue testing unit and internal pressure loading unit, it is also possible to conduct the simulation tests to investigate effects of pressure change with burn-up and longitudinal load change due to operation modes and restriction of fuel rods.
blanket. The testing machine was designed to investigate thermal-fatigue behavior under biaxial stress condition. The testing machine consists of the temperature distribution control unit, low cycle fatigue testing unit and internal pressure loading unit, it is also possible to conduct the simulation tests to investigate effects of pressure change with burn-up and longitudinal load change due to operation modes and restriction of fuel rods.
Shelley, A.; Kugo, Teruhiko; Shimada, Shoichiro*; Okubo, Tsutomu; Iwamura, Takamichi
JAERI-Research 2004-002, 47 Pages, 2004/03
Neutronic study has been done for a PWR-type reduced-moderation water reactor with seed-blanket fuel assemblies to achieve a high conversion ratio, a negative void coefficient and a high burnup by using a MOX fuel. The results of the precise assembly burnup calculations show that the recommended numbers of seed and blanket layers are 15(S15) and 5(B5), respectively. By the optimization of axial configuration, the S15B5 assembly with the seed of 1000 2 mm high, internal blanket of 150 mm high and axial blanket of 400
2 mm high, internal blanket of 150 mm high and axial blanket of 400 2 mm high is recommended. In this configuration, the conversion ratio is 1.0 and the core average burnup is 38 GWd/t. The S15B5 assembly can attain the core average burnup of 45 GWd/t by decreasing the height of seed to 500
2 mm high is recommended. In this configuration, the conversion ratio is 1.0 and the core average burnup is 38 GWd/t. The S15B5 assembly can attain the core average burnup of 45 GWd/t by decreasing the height of seed to 500 2 mm, however, the conversion ratio becomes 0.97. The void and fuel temperature coefficients are negative for both of the configurations. Effect of metal or T-MOX (PuO
2 mm, however, the conversion ratio becomes 0.97. The void and fuel temperature coefficients are negative for both of the configurations. Effect of metal or T-MOX (PuO +ThO
+ThO ) fuel has been also investigated. Metal improves the conversion ratio but makes the void coefficient worse. T-MOX improves the void coefficient, but decreases the conversion ratio.
) fuel has been also investigated. Metal improves the conversion ratio but makes the void coefficient worse. T-MOX improves the void coefficient, but decreases the conversion ratio.
Shelley, A.; Shimada, Shoichiro*; Kugo, Teruhiko; Okubo, Tsutomu; Iwamura, Takamichi
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 224(3), p.265 - 278, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:66.87(Nuclear Science & Technology)Parametric studies have been done for a PWR-type reduced-moderation water reactor (RMWR) with seed-blanket fuel assembles to achieve a high conversion ratio, negative void reactivity coefficient and a high burnup. It was found that 50 to 60% of seed in a seed-blanket assembly has higher conversion ratio. The number of seed-blanket layers is 20, in which the number of seed layers is 15 and blanket layers is 5. The fuel assembly with the height of seed of 1000mm 2, internal blanket of 150 mm and axial blanket of 400mm
2, internal blanket of 150 mm and axial blanket of 400mm 2 is recommended. The conversion ratio is 1.0 and the average burnup in core region is 38.2 GWd/t. The enrichment of fissile Pu is 14.6 wt%. The void coefficient is +21.8 pcm/% void, however, it is expected that the void coefficient will be negative if the radial neutron leakage is taken into account. It is also possible to use this fuel assembly for a high core averaged burnup of 45GWd/t, however, the height of seed must be 500mm
2 is recommended. The conversion ratio is 1.0 and the average burnup in core region is 38.2 GWd/t. The enrichment of fissile Pu is 14.6 wt%. The void coefficient is +21.8 pcm/% void, however, it is expected that the void coefficient will be negative if the radial neutron leakage is taken into account. It is also possible to use this fuel assembly for a high core averaged burnup of 45GWd/t, however, the height of seed must be 500mm 2 to improve the void coefficient. The conversion ratio is 0.97 and void coefficient is +20.8 pcm/%void.
2 to improve the void coefficient. The conversion ratio is 0.97 and void coefficient is +20.8 pcm/%void.
Okubo, Tsutomu
Konsoryu, 17(3), p.228 - 235, 2003/09
The Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor is supposed to realize plutonium multiple recycling, and furthermore, plutonium breeding cycle, based on the well-established Light Water Reactor technologies. In the present paper, the overview of the design study is presented and the related R&D issues are introduced, especially focusing on the thermal hydraulic activities.
Nakatsuka, Toru; Tamai, Hidesada; Kureta, Masatoshi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Akimoto, Hajime; Iwamura, Takamichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Global Environment and Advanced Nuclear Power Plants (GENES4/ANP 2003) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2003/09
It is important to evaluate thermal margin of the tight lattice core in the Reduced-Moderation Water reactor (RMWR). In the present study, to assess the applicability of subchannel analysis for tight lattice cores, tight lattice CHF experiments were analyzed with COBRA-TF code. For the axial uniform heated rod bundle, the code gives good prediction of critical power for mass velocity of around 500kg/(m s), while the code underestimates it for lower mass velocity and overestimates for higher mass velocity. The predicted BT position was outer channels and differed from the measured position. For the axially double-humped heated bundle, the code gives good prediction for mass velocity of around 200kg/(m
s), while the code underestimates it for lower mass velocity and overestimates for higher mass velocity. The predicted BT position was outer channels and differed from the measured position. For the axially double-humped heated bundle, the code gives good prediction for mass velocity of around 200kg/(m s), and overestimates for higher mass velocity. It turned out that the two-phase multiplier of friction loss have a large influences on the flow distribution among the subchannels. To improve the calculation accuracy, it is required to predict precisely the flow distribution including the prediction of pressure distribution in a tight lattice bundle.
s), and overestimates for higher mass velocity. It turned out that the two-phase multiplier of friction loss have a large influences on the flow distribution among the subchannels. To improve the calculation accuracy, it is required to predict precisely the flow distribution including the prediction of pressure distribution in a tight lattice bundle.
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Akimoto, Hajime
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2003-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu, Vol.3, p.247 - 248, 2003/08
We start R&D project to develop the predictable technology for thermal-hydraulic performance of Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) in collaboration with power company/reactor vendor/university since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources, multiple recycling of plutonium, high burn-up and long operation cycle, based on matured BWR technologies. MOX fuel assemblies with tight lattice arrangement are used to increase the conversion ratio by reducing the moderation of neutron energy. Increasing the in-core void fraction also contributes to the reduction of neutron moderation. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR because of the tight lattice configuration. This series presentation focuses on the feasibility study and shows the R&D plan using large-scale test facility and advanced numerical simulation technology.
Nakatsuka, Toru; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Iwamura, Takamichi
JAERI-Conf 2001-013, 263 Pages, 2001/09
The research on Reduced-Moderation Water Reactors (RMWRs) has been performed in JAERI for the development of future innovative reactors. The 4th workshop on the RMWRs was held on March 2, 2001 aimed at information exchange between JAERI and other organizations. This report includes the eight original papers presented at the workshop and summaries of the questions and answers for each lecture. Titles of the papers are“Recent Situation of Research on Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor“, “Analysis on Electricity Generation Costs of Reduced Moderation Water Reactors“,“Reprocessing Technology for Spent Mixed-Oxides Fuel from LWR“,“Micro Reactor Physics of MOX Fueled LWR“, “Fast Reactor Cooled by Supercritical Light Water “, “Phase 1 of Feasibility Studies on Commercialized Fast Breeder Reactor Cycle System“, “Integral Type Small PWR with Stand-alone Safety“ and “Utilization of Plutonium in Reduced-Moderation Water Reactors“.
Okubo, Tsutomu; Takeda, Renzo*; Iwamura, Takamichi; Yamamoto, Kazuhiko*; Okada, Hiroyuki*
Proceedings of International Conference on Back-End of the Fuel Cycle: From Research to Solutions (GLOBAL 2001) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2001/09
An advanced water-cooled reactor concept named the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) has been proposed to attain a high conversion ratio more than 1.0 and to achieve the negative void reactivity coefficient. At present, several types of design concepts satisfying both the design targets have been proposed based on the evaluation for the fuel without fission products and minor actinides. In this paper, the feasibility of the RMWR core is investigated and confirmed for the plutonium multiple recycling under advanced reprocessing schemes with low decontamination factors as proposed for the FBR fuel cycle.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Shimada, Shoichiro*; Usui, Shuji*; Shirakawa, Toshihisa*; Nakatsuka, Toru; Kugo, Teruhiko; Akie, Hiroshi; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Wada, Shigeyuki*
JAERI-Research 99-058, p.61 - 0, 1999/11
no abstracts in English